1. Introduction
In biometrics research, combing multiple imaging modalities has been proven to be a promising way to enhance performances of recognition. According to electromagnetic theory, hertzian waves ranging from visble light spectrum to near infrared provide increasing stronger penetravitity into objects. For hand biometrics, multi-spectrum illuminator can penetrate subcutaneous tissues at different depths in palm regions and form images of both surface skin textures and hypodemia (including palm veins). Based on this property, we design a multi-spectrum imaging device to capture correlative and complementary information of human hands.
CASIA Multi-Spectral Palmprint Image Database V1.0 (or CASIA-MS-PalmprintV1 for short) is released in order to promote research and progress on multiple spectral imaging of biometric modalities.
2. Brief Descriptions of the Database
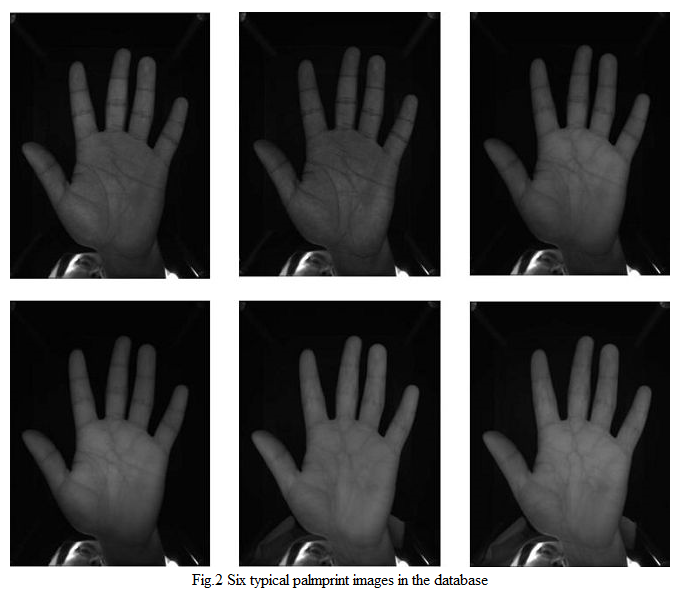
CASIA Multi-Spectral Palmprint Image Database contains 7,200 palm images captured from 100 different people using a self-designed multiple spectral imaging device,as shown in Fig.1. All palm images are 8 bit gray-level JPEG files. For each hand, we capture two sessions of palm images. The time interval between the two sessions is more than one month. In each session, there are three samples. Each sample contains six palm images which are captured at the same time with six different electromagnetic spectrums. Wavelengths of the illuminator corresponding to the six spectrums are 460nm, 630nm, 700nm, 850nm, 940nm and white light respectively. Between two samples, we allow a certain degree of variations of hand postures. Through that, we aim to increase diversity of intra-class samples and simulate practical use.
In our device, there are no pegs to restrict postures and positions of palms. Subjects are required to put his palm into the device and lay it before a uniform-colored background. The device supplies an evenly distributed illumination and captures palm images using a CCD camera fixed on the bottom of the device. We design a control circuit to adjust spectrums automatically. Six typical palmprint images in the database are shown in Fig.2